Our main products: Amino silicone, block silicone, hydrophilic silicone,all of their silicone emulsion,wetting rubbing fastness improver, water repellent(Fluorine free,Carbon 6,Carbon 8), demin washing chemicals(ABS, Enzyme, Spandex protector, Manganese remover), Main export countries: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Türkiye, Indonesia, Uzbekistan, etc.,more detail please contact : Mandy +86 19856618619 (Whatsapp )
The commonly used surfactants are low molecular weight compounds with a molecular weight of several hundred. With many hot topics such as enhanced oil recovery The in-depth research on drug carrier and controlled release, biological simulation, polymer LB film, medical polymer materials (anticoagulant), lotion polymerization, etc., has increasingly diversified and high-performance requirements for surfactants. Surfactant polymer compounds have become the focus of attention.
Substances with a molecular weight of several thousand or more and surface activity are usually referred to as high molecular weight surfactants. Similar to ordinary surfactants, there is no standard classification system for polymer surfactants. According to the classification of low molecular weight surfactants based on their ionicity in water, they can be classified into anionic, cationic, zwitterionic, and nonionic types. According to whether micelles are formed in the solution, it can be divided into soap and water-soluble polymer surfactants.
Polysoap
The vast majority of soaps are charged, similar to polyelectrolytes. In fact, most soaps are products of hydrophobic modification of polyelectrolytes and are generally insoluble in water. There are currently several types of synthesized soaps (where R represents long-chain alkyl):
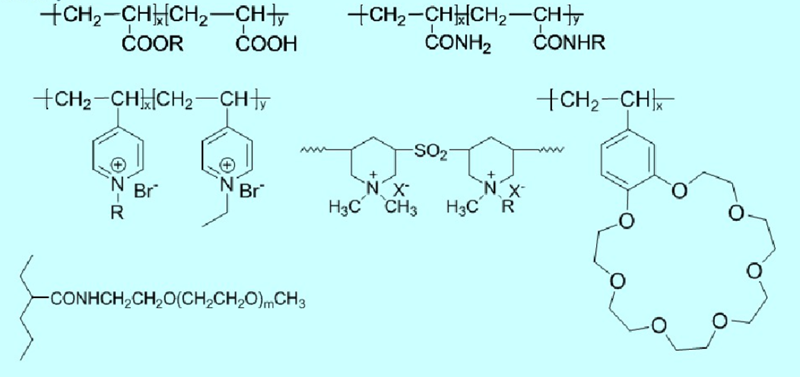
Water soluble polymer surfactant
Polymer surfactants that do not form micelles in solution are generally water-soluble polymer surfactants. According to their sources, they can be divided into three categories: natural, semi synthetic, and synthetic polymer surfactants.
Natural polymers such as various common tree gums, starches, microbial fermented polysaccharides, etc;
Semi synthetic polymers are various polymers obtained by chemical modification of starch, cellulose, and protein, such as cationic starch, methyl cellulose, etc;
Synthetic polymers are obtained by polymerizing monomers derived from petrochemicals, such as polyacrylamide derivatives, polyacrylic acid, etc.
Classification of Polymer Surfactants
According to their ionicity in water, they can be classified into anionic, cationic, zwitterionic, and non-ionic types.
Anionic polymer surfactant
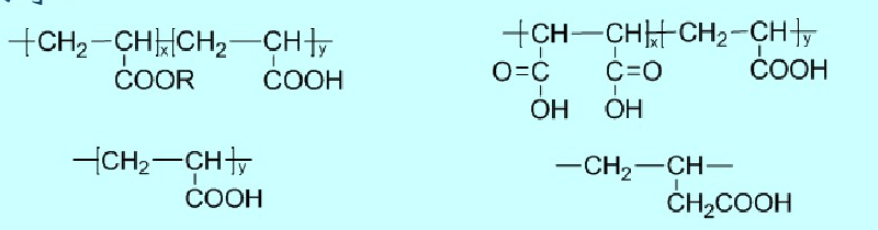
(1) Typical carboxylic acid type polymers include polyacrylic acid and its copolymers, butenoic acid and its copolymers, acrylic acid maleic anhydride copolymers, and their partially saponified products.
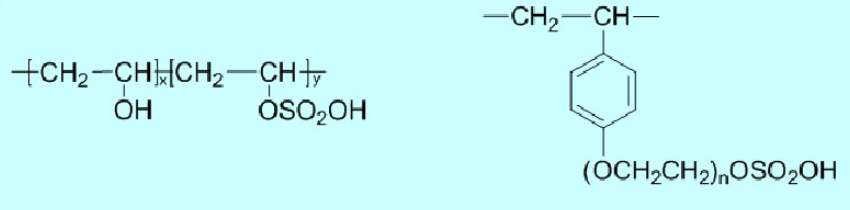
(2) Typical polymers of sulfate ester type include:
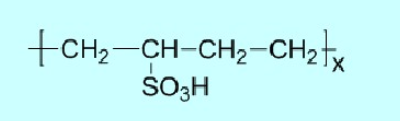
(3) Sulfonic acid type
Some sulfonated polystyrene, benzenesulfonic acid formaldehyde condensate, naphthalene sulfonic acid formaldehyde condensate, sulfonated polybutadiene, etc. Lignosulfonate is also a sulfonic acid type polymer surfactant. Typical sulfonic acid based polymer surfactants include:
Cationic polymer surfactant
Amine salts or polyamines such as polyethyleneimine, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polymaleimide, and their derivatives. Typical polymers include:
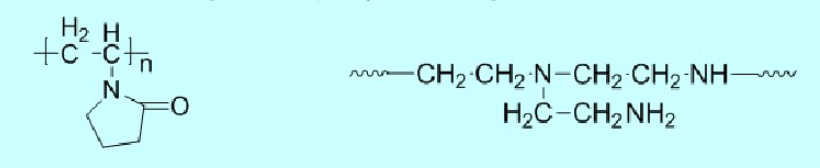
(2) Quaternary ammonium salt
Such as quaternized polyacrylamide, polyvinyl pyridine salt, polydimethylamine epichlorohydrin, etc. Quaternary ammonium polymer surfactants exhibit cationic properties in acidic, neutral, and alkaline aqueous media. Representative products include:
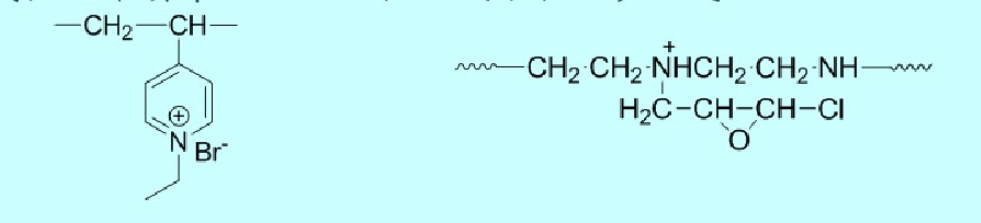
Amphoteric polymer surfactant
The main varieties include acrylic vinyl pyridine copolymer, acrylic acid, cationic acrylic ester copolymer, amphoteric polyacrylamide, etc., such as:
Non ionic polymer surfactants
The main varieties include polyvinyl alcohol and its partially esterified or acetalized products, such as modified polyacrylamide, maleic anhydride copolymer, polyacrylate, polyether, polyethylene oxide propylene oxide, water-soluble phenolic resin, amino resin, etc.
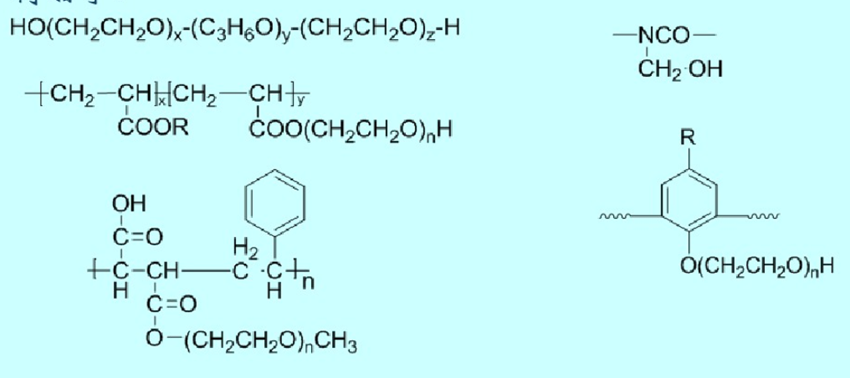
Structure and Properties of Polymer Surfactants
The surface activity of polymer surfactants depends on the morphology of the macromolecules in solution, which is closely related to the amphiphilic chemical structure, composition ratio, and relative molecular weight of the macromolecules.
Block type surfactant
Multi block hydrophobic segments are distributed on the main chain of macromolecules, and an appropriate length of hydrophobic hydrophilic sequence will effectively prevent self aggregation of hydrophobic segments (forming single-molecule micelles) or intermolecular aggregation (multi molecule aggregation)
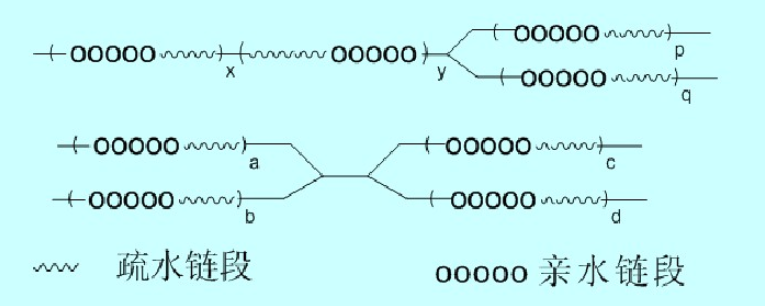
Comb shaped surfactant
Comb shaped surfactants have the advantages of easy preparation and diverse varieties. Surfactants can be obtained by homopolymerization or copolymerization of both sexes and amphiphilic monomers. Depending on the position of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups, they exhibit different branched chemical structures.
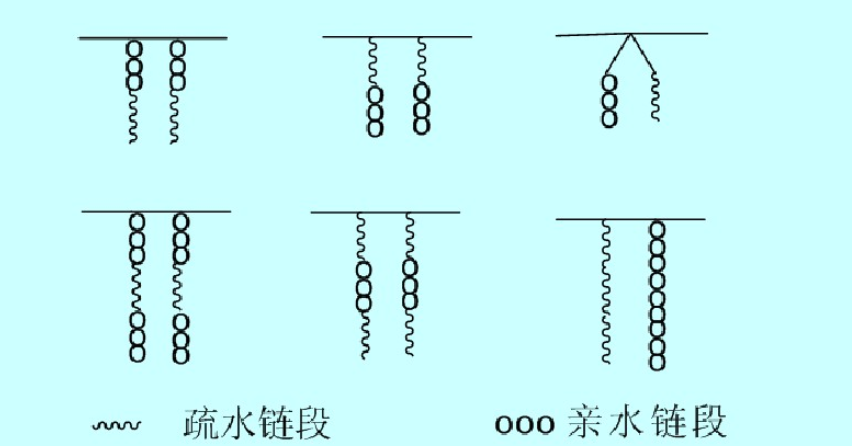
Due to the presence of hydrophilic groups on the side chains, the aggregation and association of hydrophobic segments are hindered. Even in the already formed micelles, compared to the tightly packed core micelles, the interior is relatively loose and still contains a large number of water molecules, thus exhibiting high surface activity; Meanwhile, due to the configuration, amphiphilic branches can hinder the binding of hydrophobic main chains composed of methylene and methylene groups, allowing them to participate in interfacial adsorption.
Research has shown that any factor that increases the rigidity of molecular chains while maintaining solubility is beneficial for the stretching of macromolecules in the solution and may enhance the surface activity of polymers.
Application of Polymer Surfactants
Application in textile printing and dyeing industry

Polyether based polymer surfactants are often used as low foaming detergents, emulsifiers, dispersants, defoamers, antistatic agents, wetting agents, printing and dyeing agents, etc; Polyvinyl alcohol and other macromolecular compounds are widely used as thickeners and protective colloids in the preparation of lotion printing and dyeing auxiliaries; Cellulose derivatives such as carboxymethyl cellulose are used in detergents as anti fouling agents; Lignosulfonate and phenolic condensate sulfonate are used as dispersants for insoluble dyes.
Post time: Jan-09-2025

